Functional Diagnostics Room
The Functional Diagnostics Room is a structural unit of the Russian National Center for Pediatric Surgery and provides a wide range of modern highly informative diagnostic research methods.
During the year, the children’s center performs about 6,000 diagnostic tests.


Employees of the functional diagnostics room
Doctors from the first and highest qualification categories work in the functional diagnostics room. The cabinet staff has extensive work experience. Doctors constantly take part in conferences, training, work in other clinics, etc.

Kirill Yurievich
endoscopist
(Head of the Diagnostic Department),
highest qualification category, PhD

Ekaterina Sergeevna
pediatrician

Ekaterina Dmitrievna
intern doctor

Evgenia Anatolyevna
doctor of functional diagnostics

SNIGIREVA
Elena Vasilyevna
nurse (senior)
Range of services
12-lead electrocardiography (ECG)
an extended protocol is used with the registration of ECG lying, standing and with physical activity (squats)
Medicinal samples with vegetotropic and antiarrhythmic drugs
ECG registration is carried out to assess the effectiveness and effect of various drugs in various cardiac arrhythmias
Transesophageal electrophysiological examination (TEEPE)
This study is indicated for patients with attacks of sudden onset of rapid heartbeat (paroxysmal tachycardia) that cannot be registered on an ECG and patients for differential diagnosis of bradycardia and other diseases. During the study, a tachycardia attack is provoked, which is recorded and analyzed. As a result, the presence of tachycardia is not only confirmed and documented, but its type is also determined. This is an important point in the further treatment of the patient, as well as in determining the indications for radical treatment of tachycardia – radiofrequency ablation of the tachycardia focus
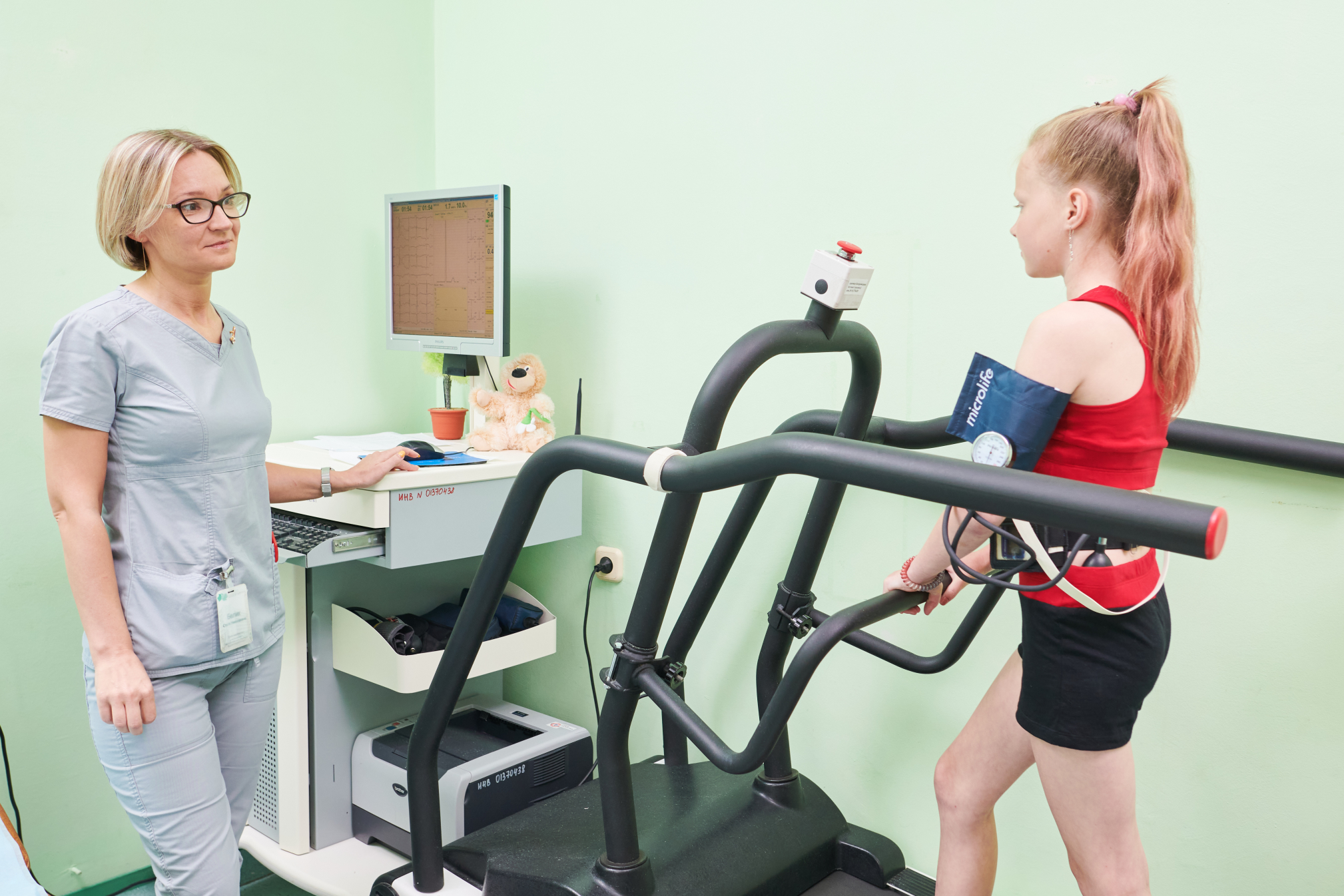
Treadmill test - a test with dosed physical activity (treadmill test - ``treadmill``)
recording of ECG and blood pressure during normalized physical activity. Different research protocols are used depending on age, disease and physical condition. patient preparation. The tolerance to physical activity, the response to the load of heart rate and other numerical and qualitative indicators of ECG, the dynamics of cardiac arrhythmias, the reaction of blood pressure to physical activity are evaluated. the load. The method with limitations is used in patients with syncopal conditions of unknown origin to identify the connection with cardiac arrhythmias
Daily monitoring, ECG (HM)
ECG registration within 24-48 hours in 3 leads. The method allows for a long period of time to evaluate various numerical and qualitative parameters of the ECG, the presence of cardiac arrhythmias, the effectiveness of AAT, LDC during the day (circadian). The method allows to identify rare ECG phenomena. Important additional criteria for the analysis are indicators of heart rate variability, turbulence. Normative indicators have been developed for children of all age groups
Daily Blood Pressure Monitoring (DBPM)
- measurement of blood pressure during the day at short intervals (15-30 min.) during the patient’s normal activity during the day and during sleep at night, with further processing of the data obtained on a computer
- daily blood pressure monitoring allows you to track daily fluctuations in blood pressure, identify hypertension, malignant forms of which lead to strokes and heart attacks. It allows you to carry out the correct hourly selection of medicines and monitor the adequacy of their effects
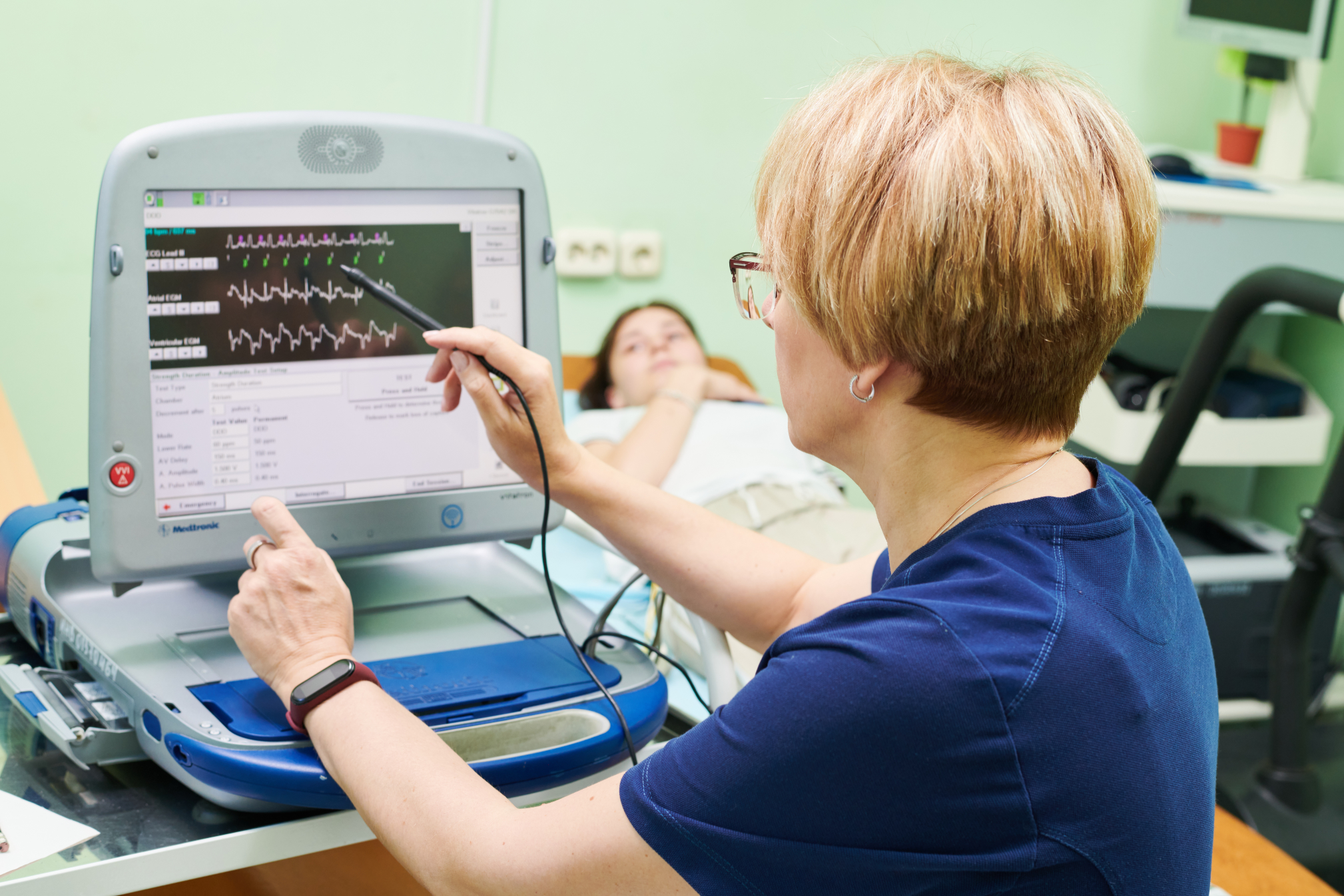
Programming of pacemakers (PP)
Medtronic, St.Jude and cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) – the main task of a pacemaker (pacemaker) is to maintain or impose a heart rate on a patient whose heart is not beating often enough, or there is an electrophysiological disconnection between the atria and ventricles (atrioventricular block)
24-hour pH Metric with Impedance - Daily pH Metric
Daily pH measurement is the process of measuring acidity (concentration of hydrogen ions) directly in the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach) using a pH probe and an appropriate recording device during the day.
Daily pH impendance measurement is a method for registering liquid and gas intraesophageal reflux, based on measuring the resistance (impedance) that the contents entering the lumen of the esophagus exert during the day. It allows you to record the total number of episodes of gastroesophageal reflux during the day, regardless of the type of acidity, determine their physical composition, the height of spread, the rate of purification of the esophagus from reflux and the duration of each episode of reflux.
The Bravo wireless (capsule) pH monitoring system is designed to measure gastrointestinal pH and monitor gastric reflux in adults and children from the age of 4.
High-resolution esophageal manometry = the “gold” standard for assessing the motor function of the esophagus and the condition of the esophageal sphincters. Allows you to obtain accurate quantitative and qualitative data on intraluminal pressure, coordination and motility of the muscles of the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter
Anorectal manometry with 3D reconstruction
a method of qualitative and quantitative assessment of the functioning of the organs of the anorectal region, providing defecation and retention of intestinal contents. It allows to assess the tone of the anorectal muscle complex and the coordination of contractions of the rectum and anal sphincters, based on the registration of pressure in the rectum and the pressure profile in the rectum and anus
Esophageal manometry
high-resolution esophageal manometry makes it possible to assess the contractile activity of the thoracic esophagus, its peristalsis, the strength of contractions, and the coordination of peristalsis with the work of the lower and upper esophageal sphincters. This method is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of achalasia of the cardia, distal esophagospasm, ineffective motility of the esophagus (for example, in systemic scleroderma, diabetes mellitus)
Spirography (spirography, the function of external respiration)
one of the main diagnostic methods in pulmonology and therapy for assessing the functional state of the lungs. The method allows you to measure lung volume, exhalation volume in one second and exhalation rate. After conducting the study, the doctor can assess how much the disease has changed the ability of the lungs to fill with air and the ability of the bronchi to pass air during inhalation and exhalation. Spirometry is a study of the function of external respiration
